Introduction to Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are essential components of modern industrial automation systems, revolutionizing the way manufacturing processes are controlled and monitored. In this chapter, we will explore the definition, historical background, evolution, and advantages of PLCs over traditional relay-based control systems.
Definition and Purpose of PLCs in Industrial Automation:
PLCs are specialized digital computers designed to automate control processes in industrial environments. They are programmable devices capable of executing logic functions, sequencing tasks, and controlling various electromechanical processes. PLCs play a crucial role in automating tasks such as machine operation, production line control, and process monitoring across a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, automotive, pharmaceuticals, and energy.
Historical Background and Evolution of PLC Technology:
The concept of PLCs emerged in the late 1960s as a solution to the limitations of traditional relay-based control systems, which were cumbersome, inflexible, and difficult to modify. The first PLC, known as the Modicon 084, was introduced by Modicon (now part of Schneider Electric) in 1969. It revolutionized industrial automation by offering a compact, programmable alternative to relay logic control systems.
Over the years, PLC technology has evolved significantly, with advancements in computing power, memory capacity, and communication capabilities. Today’s PLCs are highly sophisticated devices capable of performing complex control tasks, integrating with other automation systems, and facilitating real-time data exchange for enhanced productivity and efficiency.
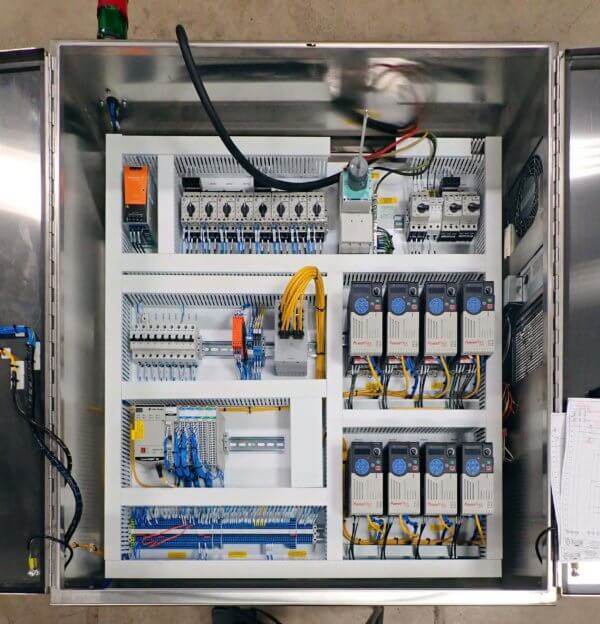
Advantages of Using PLCs Over Traditional Relay-Based Control Systems:
There are several key advantages of using PLCs over traditional relay-based control systems:
- Flexibility: PLCs offer greater flexibility in programming and configuring control logic, allowing for easier modifications and adaptations to changing process requirements.
- Reliability: PLCs are more reliable than relay-based systems, with fewer moving parts and reduced susceptibility to mechanical wear and tear.
- Space-saving: PLCs are compact devices that require less physical space compared to relay panels, saving valuable floor space in industrial facilities.
- Integration: PLCs can easily integrate with other automation components, such as sensors, actuators, and human-machine interfaces (HMIs), enabling seamless communication and coordination of control functions.
- Diagnostics: PLCs offer advanced diagnostic capabilities, allowing operators to monitor system performance, troubleshoot faults, and quickly identify and resolve issues.
- Cost-effectiveness: While PLCs may have a higher initial investment compared to relay-based systems, they offer long-term cost savings through improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and easier maintenance.

Conclusion:
In summary, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) have transformed the landscape of industrial automation, offering unparalleled flexibility, reliability, and efficiency compared to traditional relay-based control systems. By understanding the definition, historical background, evolution, and advantages of PLCs, we can appreciate their significance in modern manufacturing and engineering applications.
